Imagery and repetition are aspects offormality.purpose.tone.word choice. that play a pivotal role in shaping the impact of literary works. This essay delves into their multifaceted nature, exploring how they enhance the reader’s experience and convey the author’s intended message.
Imagery transports readers into vivid worlds, evoking sensory experiences and creating a sense of immersion. Repetition, on the other hand, establishes rhythm, emphasizes key ideas, and fosters a sense of unity. Together, these elements orchestrate the tone and mood of a work, influencing the reader’s emotional response.
Imagery

Imagery is a literary device that uses vivid and descriptive language to create a sensory experience for the reader. It appeals to the five senses—sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch—to create a strong mental image in the reader’s mind.
Imagery can enhance the reader’s experience by:
- Creating a sense of place, time, and character
- Eliciting emotions and creating a desired mood
- Making the writing more concrete and memorable
There are many different types of imagery, including:
- Visual imagery: Appeals to the sense of sight
- Auditory imagery: Appeals to the sense of hearing
- Olfactory imagery: Appeals to the sense of smell
- Gustatory imagery: Appeals to the sense of taste
- Tactile imagery: Appeals to the sense of touch
Imagery can be used effectively in all genres of literature, from poetry to prose. By creating vivid and memorable images, authors can transport readers to different worlds, evoke powerful emotions, and create a lasting impact.
Repetition: Imagery And Repetition Are Aspects Offormality.purpose.tone.word Choice.
Repetition is a literary device that involves the repeated use of words, phrases, or ideas. It can be used to create emphasis, rhythm, and unity.
There are many different forms of repetition, including:
- Anaphora: The repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses or sentences
- Epiphora: The repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences
- Symploce: The repetition of a word or phrase at both the beginning and end of a clause or sentence
- Anadiplosis: The repetition of a word or phrase at the end of one clause or sentence and the beginning of the next
- Epanalepsis: The repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning and end of a clause or sentence
Repetition can be used effectively in all genres of literature, from poetry to prose. By repeating words, phrases, or ideas, authors can create emphasis, rhythm, and unity, and reinforce important themes or ideas.
Formality

Formality is a literary device that refers to the level of formality in the language used in a piece of writing. It can range from very formal to very informal.
The level of formality in a piece of writing can have a significant impact on the tone and style of the work. Formal language is often used in academic writing, legal documents, and other serious works. Informal language is often used in fiction, poetry, and other creative works.
There are many different factors that can affect the level of formality in a piece of writing, including:
- The genre of the work
- The intended audience
- The author’s personal style
By choosing the appropriate level of formality, authors can create a desired tone and style for their work.
FAQ Section
What is the primary function of imagery in literature?
Imagery appeals to the senses, creating vivid mental images that enhance the reader’s experience and deepen their understanding of the narrative.
How does repetition contribute to the effectiveness of literary works?
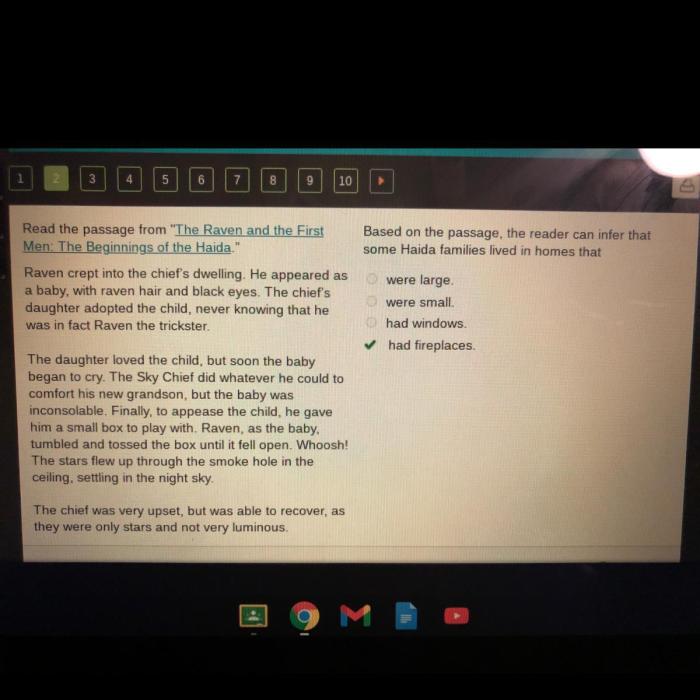
Repetition establishes rhythm, emphasizes key ideas, and creates a sense of unity, enhancing the overall impact and memorability of the work.

