An induced draft air cooled condenser stands as a cornerstone in the realm of heat exchange, offering an efficient and reliable solution for a wide range of industrial applications. This condenser harnesses the power of induced airflow to effectively dissipate heat, making it an indispensable component in numerous sectors.
Its intricate design and operational principles form the foundation of its exceptional performance, which we will explore in depth throughout this comprehensive analysis.
Definition of an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser
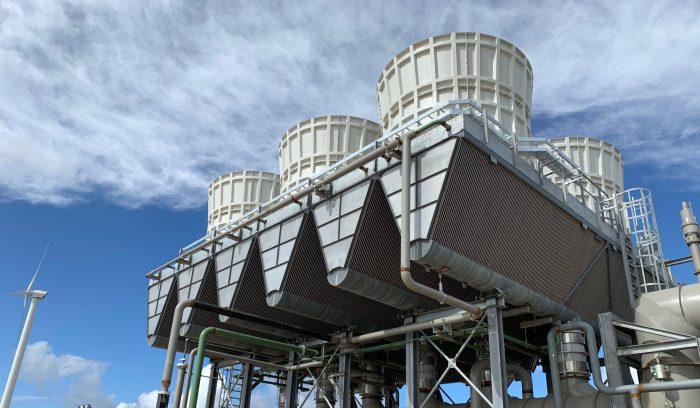

An induced draft air cooled condenser (IDACC) is a type of heat exchanger used to condense refrigerant gas into liquid by rejecting heat to the surrounding air. It consists of a bundle of finned tubes arranged in a vertical or horizontal configuration, with a fan located at the discharge end to induce airflow through the tubes.
Working Principle of an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser
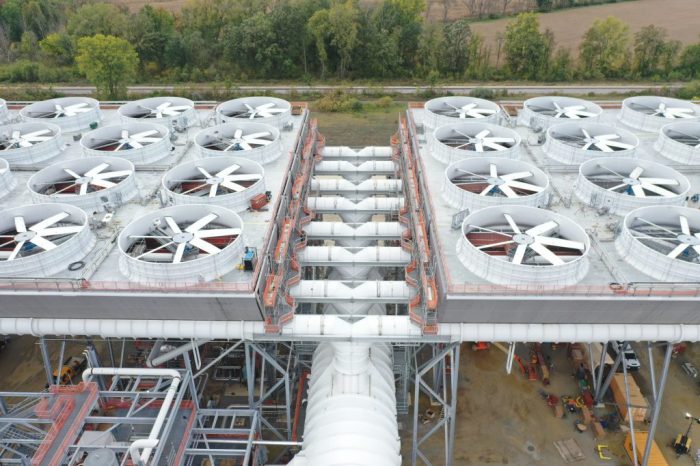

The refrigerant gas enters the condenser at a high temperature and pressure and flows through the tubes. As the gas passes through the tubes, it transfers heat to the cooler air flowing over the fins. The cooled gas condenses into a liquid and exits the condenser at a lower temperature and pressure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers, An induced draft air cooled condenser
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages ||—|—|—|| Efficiency | High efficiency, especially in dry and cold climates | Lower efficiency in hot and humid climates || Cost | Lower initial cost compared to other types of condensers | Higher operating costs due to fan power consumption || Maintenance | Relatively low maintenance requirements | Regular cleaning and inspection of fins and tubes required || Environmental impact | Environmentally friendly, as it does not use water | Noise and visual pollution due to the fan |
Design Considerations for Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers
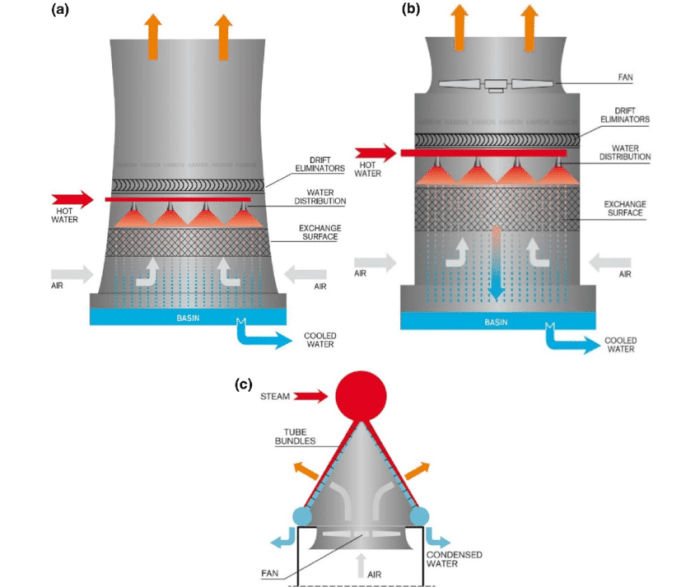
Key design parameters for IDACCs include:
Airflow rate
Higher airflow rates improve heat transfer but increase pressure drop.
Tube size
Larger tube diameters provide lower pressure drop but reduce heat transfer surface area.
Fin spacing
Closer fin spacing increases heat transfer surface area but also increases pressure drop.
Applications of Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers
IDACCs are commonly used in:
- Power plants
- Industrial refrigeration systems
- Air conditioning systems
- Data centers
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers
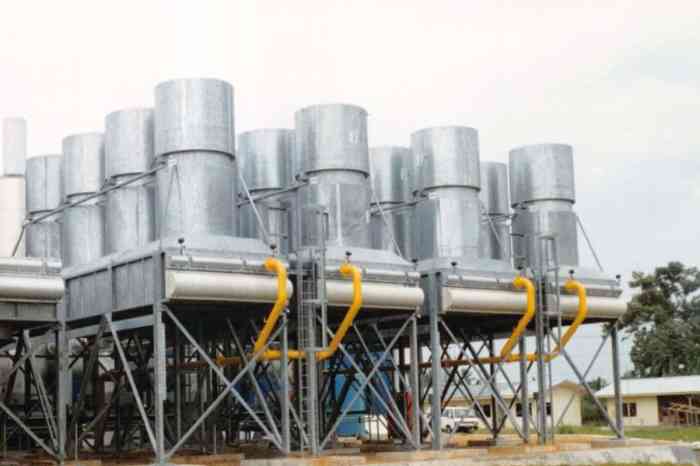

Regular maintenance of IDACCs includes:
- Cleaning of fins and tubes to remove dirt and debris
- Inspection of fan blades for damage or wear
- Monitoring of refrigerant pressure and temperature
Common troubleshooting issues include:
- Reduced heat transfer due to fouling of fins or tubes
- Fan failure or reduced airflow
- Refrigerant leaks
Answers to Common Questions: An Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser
What is the primary function of an induced draft air cooled condenser?
An induced draft air cooled condenser primarily serves to remove heat from a working fluid by utilizing induced airflow to facilitate heat transfer.
How does an induced draft air cooled condenser operate?
The condenser operates by drawing air through its tubes, which are designed to promote heat transfer from the working fluid to the air. The heated air is then expelled into the surrounding environment.
What are the key advantages of induced draft air cooled condensers?
Induced draft air cooled condensers offer several advantages, including compact size, high efficiency, low maintenance requirements, and reduced water consumption compared to evaporative condensers.