As the Cheat Sheet Phlebotomy Study Guide takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with authoritative knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Phlebotomy, the art of drawing blood, is a crucial aspect of healthcare, and this guide serves as an invaluable resource for students and practitioners alike. Delving into the intricacies of this specialized field, we will explore the techniques, equipment, and ethical considerations that define phlebotomy.
Understanding Phlebotomy
Phlebotomy is the process of collecting blood from a vein for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. Phlebotomists, the healthcare professionals who perform phlebotomy, play a crucial role in patient care by ensuring accurate and timely blood collection.
There are various blood collection methods, including venipuncture, capillary puncture, and arterial puncture. Venipuncture, the most common method, involves drawing blood from a vein in the arm using a needle and syringe or vacutainer system.
Proper patient identification is essential to prevent errors and ensure patient safety. This includes verifying the patient’s name, date of birth, and medical record number before collecting blood.
Phlebotomy Equipment and Techniques
Phlebotomy Equipment
- Gloves
- Alcohol swabs
- Tourniquet
- Needles (various gauges and sizes)
- Syringes or vacutainer system
- Blood collection tubes
- Sharps container
Venipuncture Techniques
- Apply a tourniquet to the upper arm.
- Palpate the vein and select an appropriate puncture site.
- Clean the puncture site with an alcohol swab.
- Insert the needle at a 15-30 degree angle into the vein.
- Collect the blood into the appropriate tube.
- Release the tourniquet and apply pressure to the puncture site.
- Fast for 8-12 hours before blood collection (if required).
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Avoid strenuous exercise.
- Inform the phlebotomist of any medications or supplements they are taking.
- Time of day
- Patient’s posture
- Stress
- Medications
- Diet
- Mixed thoroughly
- Stored at the appropriate temperature
- Transported promptly to the laboratory
- Incorrect patient identification
- Improper venipuncture technique
- Hemolysis (rupture of red blood cells)
- Clotted samples
- Insufficient sample volume
- Follow proper patient identification protocols.
- Use the appropriate venipuncture technique and needle size.
- Handle blood samples gently to avoid hemolysis.
- Ensure that blood samples are collected in the correct tubes.
- Collect sufficient sample volume for testing.
- Regular equipment calibration
- Use of certified reference materials
- Participation in proficiency testing programs
- Patient confidentiality
- Respect for patient autonomy
- Non-maleficence (do no harm)
- Beneficence (act in the patient’s best interests)
- Medical malpractice
- Negligence
- Assault and battery
Needle Gauges and Sizes
Needle gauges and sizes vary depending on the patient’s vein size and the amount of blood required. Larger gauge needles (lower numbers) are used for collecting larger volumes of blood, while smaller gauge needles (higher numbers) are used for collecting smaller volumes.
Pre-Analytical Considerations
Patient Preparation
Adequate patient preparation is crucial to ensure accurate blood test results. Patients should be instructed to:
Factors Affecting Blood Test Results
Several factors can affect blood test results, including:
Handling and Transporting Blood Samples
Proper handling and transportation of blood samples are essential to maintain sample integrity. Blood samples should be:
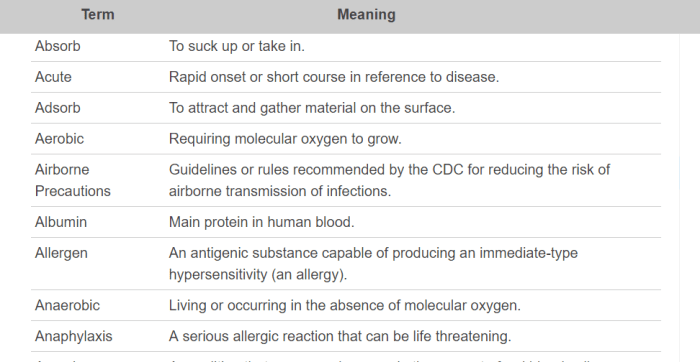
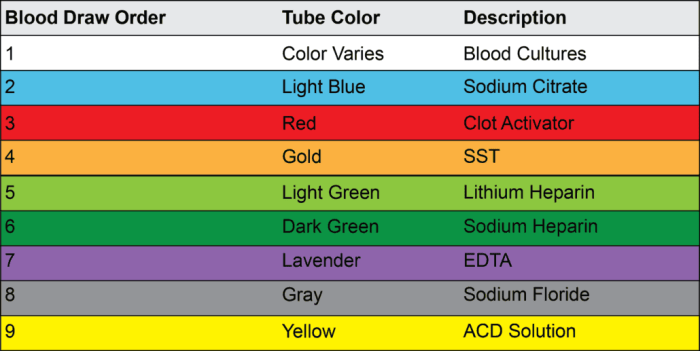
Common Blood Collection Tubes
| Tube Type | Color | Additives | Intended Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red Top | Red | No additives | Serum |
| Yellow Top | Yellow | ACD | Plasma |
| Lavender Top | Lavender | EDTA | Whole blood |
| Green Top | Green | Heparin | Plasma |
| Blue Top | Blue | Sodium Citrate | Coagulation studies |
Each tube contains specific additives that prevent blood clotting or preserve the integrity of certain blood components.
Troubleshooting and Error Prevention
Common Errors in Phlebotomy
Troubleshooting and Error Prevention
Quality Control Measures
Quality control measures are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of blood test results. These measures include:
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Ethical Principles
Phlebotomists are bound by ethical principles that include:
Legal Implications
Improper blood collection can have legal implications, including:
Patient Confidentiality, Cheat sheet phlebotomy study guide
Patient confidentiality is of utmost importance in phlebotomy. Phlebotomists must adhere to privacy regulations and ensure that patient information is protected.
FAQs: Cheat Sheet Phlebotomy Study Guide
What is the primary role of a phlebotomist?
Phlebotomists are healthcare professionals responsible for drawing blood from patients for diagnostic testing.
What are the different types of blood collection methods?
Common blood collection methods include venipuncture, capillary puncture, and arterial puncture.
Why is proper patient identification crucial in phlebotomy?
Correct patient identification ensures that the blood sample is accurately attributed to the intended patient, preventing errors and ensuring patient safety.
